Hearing Loss
Hearing Loss Overview
Hearing loss is one of the most common physical disorders in the world, affecting more than 500 million people around the globe. According to the World Health Organization, one in three people over the age of 65 has some form of hearing loss, though it can happen to anyone at any age. It is a complex condition that can have a significant impact on your life, which is why it's so important to understand hearing loss and be aware of the risk factors. Knowing what causes hearing loss and how it can be prevented or treated is essential for maintaining your hearing health.
Types of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss may be classified into two main categories (conductive and sensorineural), with two other less prevalent types (mixed and central), depending on the underlying cause.
Conductive Hearing Loss
Conductive hearing loss occurs when sound cannot pass through the outer or middle ear due to some physical blockage, such as earwax build-up or fluid accumulation in the middle ear space.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss results from direct damage or deterioration of the nerves responsible for carrying sound signals from our ears to our brains.
Mixed hearing loss is a combination of both conductive and sensorineural elements, while central hearing loss involves complications or damage to the brain itself, making it difficult to process sound properly.
Common Causes of Hearing Loss
The most common cause of hearing loss is age-related deterioration which often begins in one's mid-50s. Other causes include exposure to loud noises over long periods of time (such as working in a noisy environment without proper protection), certain medications, head injuries, genetic factors, and infections such as meningitis or measles.

Common Symptoms of Hearing Loss
The most common symptom of both major types of hearing loss is difficulty understanding speech in noisy environments. People with hearing loss may also have difficulty following conversations or struggle to hear high-pitched tones, such as those produced by birds chirping or children laughing. Some individuals may even experience ringing in their ears - known as tinnitus and dizziness - which could indicate a more serious issue with their hearing health.

Risk Factors for Hearing Loss
Age plays a major role in hearing loss – as you get older, your risk of developing a hearing impairment increases exponentially. Other risk factors include occupational exposure to loud noises (such as machinery), family history of deafness or impairment, smoking cigarettes or cigars, taking certain medications that are known to cause damage to the ears, and being born with congenital birth defects. Additionally, other illnesses, such as diabetes and high blood pressure, can increase your risk of developing a hearing impairment.
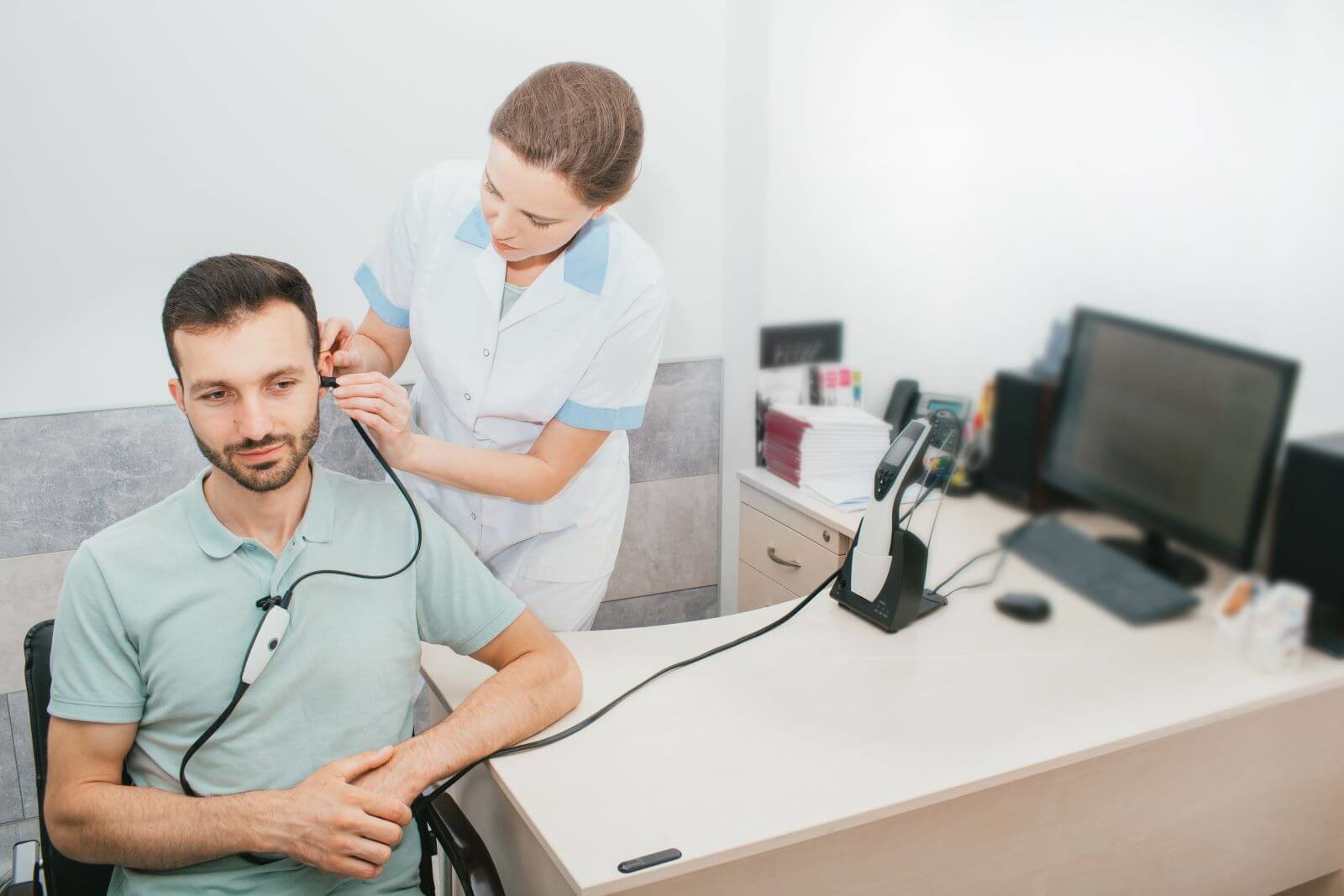

Treatment Options for Hearing Loss
The first step in treating hearing loss is visiting us. Our audiologist will perform a comprehensive evaluation and recommend a treatment plan based on your individual needs. Depending on the severity and type of hearing loss, treatment options will vary. For example, solutions for conductive hearing loss - which is often considered to be easily curable - include medical intervention such as medication or surgery. On the other hand, sensorineural hearing loss is permanent and irreparable but can be effectively managed with assistive devices such as hearing aids or cochlear implants. Additionally, some people find relief from symptoms through lifestyle changes, such as avoiding loud noises and wearing protective gear while listening to music at a concert venue.
Hearing loss is a complex condition that can have a major impact on your life if not addressed properly. While aging is the most common cause of hearing problems, other conditions, such as genetic factors and head injuries, may also play a role. Additionally, there are several types of hearing loss that can be categorized based on their underlying cause (conductive, sensorineural, or mixed). If you suspect you might be experiencing symptoms associated with hearing, contact us today to schedule an appointment.
Recent Posts

They’re coming: The Future of Over the Counter Hearing Aids
Quick Read We don’t yet know what the FDA standards for over the counter hearing aids will be, but you…
mjaudseo

How to Protect Against Hearing Loss
Quick Read Your lifestyle choices are one of the most significant factors in whether, and to what extent, you will…
mjaudseo

Looking for the Top 5 Hearing Aids? Look for Audiologist Reviews Instead
Quick Read Individual experiences with any specific hearing aid will largely depend on how well they have been customized and…
